
- #Create a matrix in g docs how to#
- #Create a matrix in g docs plus#
- #Create a matrix in g docs free#
On the first page of the report, click one of the cell values. To make your report easier to read, you can add formatting to the monetary values.
#Create a matrix in g docs how to#
For details on how to access it, see "Accessing the Example Reports" in the Preface. To see a sample matrix report, open the examples folder named matrix, then open the Oracle Reports example named matrix1qb.rdf. Thus, you could quickly determine the sum of all of the salaries for clerks in department 20 and compare that value to the one for all clerks in some other department.Īs you build this example report, you will:Īdd summaries to the single-query matrix for rows and columns.Īdd a grid to add grid lines around cells. The result would be a matrix with job functions listed across the top, departments down the side, and sums of salaries in the cells. In this example, you will create report that cross tabulates salaries by job function and department. You'll also modify some field widths to ensure that the fields fit across the page.įor additional conceptual information, see Section 1.3.7, "About matrix reports", You'll modify some default settings to ensure that the column and row labels display correctly. This report uses the matrix layout style.
#Create a matrix in g docs free#
They are presented as options feel free to try both methods and settle on a favorite. These two methods yield the same results. Section 25.3, "Create a multiple-query matrix" explains how to create the same report using three queries. Section 25.2, "Create a single-query matrix" explains how to create the matrix report using one query.

You can create matrix reports with any number of queries. If you are concerned with performance issues, for example, there are alternate methods of querying data that can improve the performance of a matrix report. The queries used to select data for these sample matrix reports are not intended as definitive examples of matrix queries. Thus, the report would automatically be extended if a new job function, called RECEPTIONIST, was added to the underlying data tables. The number of columns in your report depends on the number of values contained in the columns providing the horizontal and vertical labels.
#Create a matrix in g docs plus#
Matrix reports are different from tabular reports because the number of columns is not known in advance that is, the number of columns in your report is not determined by the number of columns you specify in your SELECT statement plus the columns you create yourself. The fourth group provides the values that fill in the grid. These two groups are the children of the third group, called the cross product group, which creates the grid.

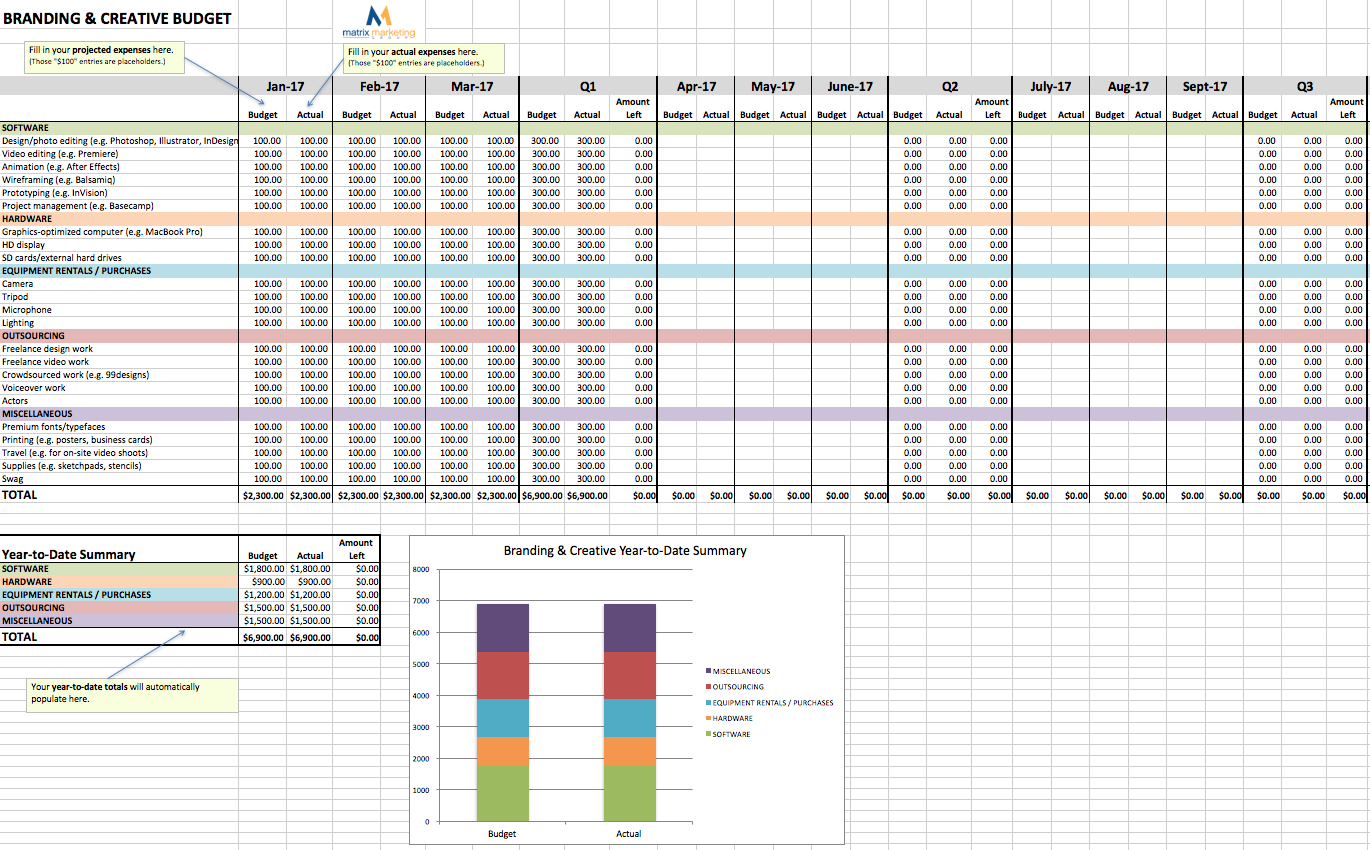
It contains four groups-one group supplies the vertical labels (department numbers) and one group supplies the horizontal labels (job identifiers). These requirements can be seen in the preceding example. The values from this group fill the cells created by the matrix. These groups furnish the "labels" of the matrix report.Īt least one group must be a "cell" group that is, it must provide the information related to the labels. You must have at least four groups in your data model.Īt least two of the groups must be within the cross product group. Of the summaries, one sums the salaries by department, one sums them by job, and one sums them for the whole report.Ĭertain requirements exist for building matrix reports: This sample matrix also contains three additions to the basic matrix: summaries have been added, zeroes replace non-existent values in the cells, and the cells themselves are surrounded by grid lines. As shown by the example report above, it contains one row of labels, one column of labels, and information in a grid format that is related to both the row and column labels. Description of "Figure 25-1 Matrix report output"Ī matrix report looks like a grid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
